Why is it called a shift to the left?
So why do we call it shift-left testing? In traditional software development models, testing typically occurs towards the end of the development process, often called the “right” side of the development timeline. However, with the rise of Agile and DevOps methodologies, there has been a shift in approach where testing is moved earlier in the development process. Hence, the term “shift to the left.”
This means that you perform testing activities, like unit testing, integration testing, and automated testing, earlier in the development lifecycle, closer to the initial stages of coding and development. Shift-left basic principles aim to identify and address defects and issues earlier in the development process, leading to faster feedback loops, reduced costs, and improved software quality.
The Importance of Shift-Left Testing
So, why do you need shift-left testing in your development process? It’s simple: addressing issues early on minimises risks, reduces costs, and improves overall product quality. With traditional approaches, you often wait until the later stages of development to tackle testing, which can mean costly fixes and delays. Shift-left testing changes that by encouraging early testing, leading to faster feedback and smoother releases.
By identifying and resolving defects earlier, you can make incremental improvements without the pressure of last-minute fixes. It helps you ensure each stage of development is robust. This shift allows you to catch critical issues when they’re faster and cheaper to fix, ultimately keeping project budgets and timelines on track. Plus, with testing integrated from the start, developers and testers collaborate more closely, sharing insights that lead to well-rounded, reliable code.
Shift-left testing also supports better user satisfaction by catching potential issues before they reach production. You’re able to release high-quality software on schedule, without surprises or hidden defects impacting your users.
Elements of Shift-Left Testing
You’re probably thinking shift-left testing is just “test early” – but here’s what actually moves the needle: weaving automation directly into your code commits and getting your devs to poke around with test cases before they even finish coding.
You need to set up feedback loops that ping your team within minutes, not hours. Teams doing this right see bug detection rates nearly double in their first sprint.
Start by having developers run one automated test locally before any commit. Simple, but it catches roughly 40% more issues upfront than traditional approaches.
The surprising part – collaboration beats automation every time. Your best shift-left results come when testers and developers actually talk through edge cases together, not from fancy CI/CD pipelines alone.
Early Testing
Early testing means conducting tests as soon as the code is written. It covers:
- Unit tests
- Integration tests
- Basic functionality checks right from the beginning.
This early intervention identifies issues before they escalate. As a result, you catch potential flaws that might otherwise slip through to later stages, where they’re costlier to fix.
For example, in large projects, small defect detection in the code’s foundation can snowball into multiple downstream errors, making it essential to find and fix issues early.
Google, for instance, has adopted early testing to support its rapid product releases, catching minor issues in foundational code that could impact performance or security later. This reduces rework and allows developers to maintain momentum by focusing on building robust features rather than firefighting bugs.
Automation
Every code push needs that immediate feedback loop, and manual testing simply can’t keep up.
Here’s what’s working: developers who embrace writing integration tests alongside their usual unit tests are catching issues nearly 60% faster. Throw in contract testing tools like Pact, and you’re validating both your code logic AND business requirements before they hit production.
Start with one integration test per feature this sprint. Don’t overthink it, just pick your most critical user flow and automate that pathway.
The teams seeing real success aren’t just testing functionality; they’re validating that what they built actually matches what stakeholders asked for. BDD frameworks make this surprisingly straightforward, turning requirements into executable tests.
Your goal? Fast, reliable feedback on every commit. When automation handles the heavy lifting, you’ll spot problems while they’re still cheap to fix.
Automated tools like Selenium and JUnit allow you to test complex scenarios in seconds. They provide early warnings of issues that would otherwise emerge in production. This enhances reliability and keeps development cycles efficient. That is why automation has become indispensable in today’s fast-paced software development.
Collaborative Approach
Shift-left testing thrives in a collaborative setup, where developers, testers, and stakeholders work together from the outset, sharing responsibility for quality. An integrated teamwork brings diverse perspectives, allowing potential issues to be identified sooner. This way, you can create a shared sense of ownership in the product’s success.
For example, Amazon’s development teams implement a collaborative “you build it, you run it” approach. This is where developers are involved in testing and monitoring their code even after it’s deployed.
This accountability enables strong quality standards, as developers understand the importance of delivering code that meets performance and reliability expectations. When everyone is engaged in early testing, here is the benefits you get:
- Feedback loops shorten
- Communication improves
- Code quality gets an early boost
So it should be no surprise to understand how important collaboration is in this case.
CI/CD
Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) are also integral to shift-left testing. In CI/CD, you automate the integration of code changes and their deployment, supporting rapid testing and feedback at every stage of development. When CI/CD is in place, every code commit triggers a series of automated tests, ensuring the new code integrates seamlessly without introducing bugs.
Netflix is a prime example of that. Its “Simian Army” automates testing and resilience checks across its infrastructure. This lets Netflix deploy updates frequently and with confidence. Additionally, it minimises downtime and ensures a seamless experience for users. Including CI/CD into shift-left testing practices allows for safe, regular releases and a robust foundation for application testing as they grow.
To implement all these principles effectively, a Test Management System (TMS) is essential. It provides a structured approach to manage, execute, and monitor tests from the earliest development stages. With a TMS, you can:
- Collaborate seamlessly
- Automate processes
- Maintain traceability
This way you ensure every test contributes to identifying and resolving issues before they escalate. And there is a perfect solution designed for all your shift-left testing needs and principles.
So why do developers recommend shift-left testing principles? Here are some significant benefits of implementing it:
- Early defect detection and resolution help reduce the costs of fixing issues later in the software development cycle.
- Improved collaboration and communication between development and testing teams with a better understanding of requirements.
- Faster feedback loops allow for more rapid identification and resolution of the bugs.
- Reduced time-to-market for software products as development and testing activities are completed simultaneously.
- Improved software quality due to the early identification of the bugs.
Overall, the list of shift-left testing benefits can be longer, but it depends on how well it is implemented. If done right, it can also improve developer & QA efficiency, productivity, and, ultimately, customer satisfaction.

Challenges of shift-left testing
We’ve talked about the benefits of shift-left testing, but what about the challenges? Moving testing earlier in the development process brings its own set of hurdles you need to be prepared for. Let’s take a look at these challenges and what they mean for your workflow.
- Skill Gaps: Your developers might feel out of their depth writing security or API tests they’ve never tackled before. Here’s what actually works – pair them with QA mentors for a few sprints and throw in some ready-to-use test templates. Teams using this approach see their early-stage bug detection nearly double within months. Start small: pick one developer to champion component testing first, then let that success spread naturally across your team.
- Increased Initial Workload: Testing from the start means more work early on, as developers balance coding and quality checks simultaneously. The dual focus can slow down initial progress, making it feel like a heavy lift. However, as processes smooth out, teams typically find that the upfront effort saves time later by catching issues early.
- Tooling Complexity: Shift-left testing relies on a suite of tools, from QA automation frameworks to CI/CD integrations. Getting these tools set up and learning their ins and outs can be complicated, especially for teams with limited resources. The right tools can make a world of difference, but the initial setup will require patience and expertise.
- Cultural Resistance: For teams used to testing at the end of the development cycle, shift-left testing is a big adjustment. It changes established workflows and may face pushback from team members who are comfortable with the old way. This shift requires leadership, training, and clear communication.
- Maintaining Test Quality: Testing early is only helpful if the tests are high-quality. Poorly written tests can give false positives or miss bugs entirely, leading to a false sense of security. Building effective tests from the start takes discipline and consistency—two things that can be challenging under tight deadlines.
- Collaboration Barriers: Shift-left testing works best with cross-functional collaboration, but not all teams are set up to work closely together. Without good communication and shared goals, early testing efforts can be less effective. Encouraging a culture of openness and regular feedback across roles is essential for making shift-left testing work well.
Overcoming these challenges, or at least being prepared for them, you will feel like you are entirely ready for this huge shift.
In DevOps practices, both shift-left and test automation are pivotal strategies to enhance software development processes and ensure high-quality software delivery. We have discussed the aim of the shift left testing strategy in the previous paragraphs. Similarly, test automation complements this approach by providing the means to execute tests rapidly and efficiently. Automated tests, including unit tests and integration tests, enable you to obtain immediate feedback on code changes, allowing you to detect bugs and vulnerabilities earlier.
Furthermore, both shift-left and test automation accelerate feedback loops within the DevOps cycle. By detecting issues early and automating testing processes, you can iterate more quickly and confidently and deliver updates to production. This iterative approach fosters continuous improvement and innovation, driving the evolution of software products in alignment with user needs and market demands.
Implementing a shift-left approach in your software development process will bring numerous benefits, including early defect detection, faster time-to-market, higher customer satisfaction, reduced costs, and better team morale.
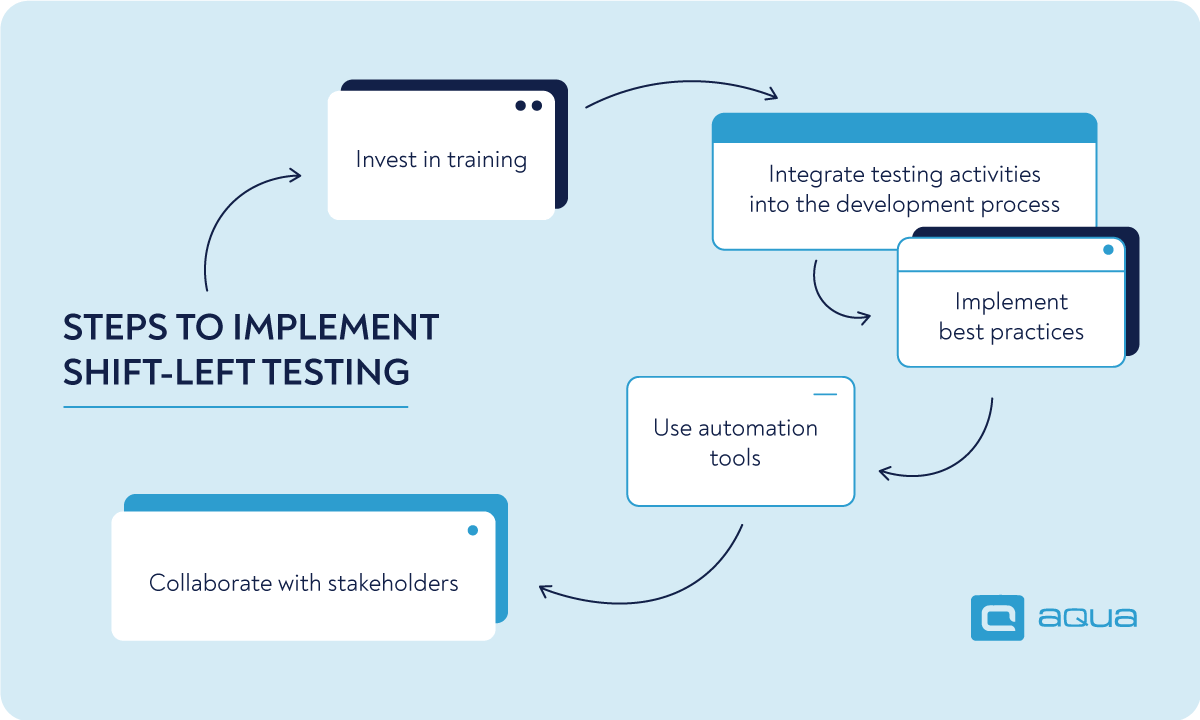
By adopting the best practices examples we provided above, you can successfully implement shift-left testing in an Agile environment and reap the rewards.
If you want to adopt these best practices in your testing, aqua’s testing strategy template is an essential tool for you. With clear requirements for every level of testing, actionable tips to improve your testing processes, and recommendations for choosing the right testing tools, this template is a comprehensive guide to ensuring that your testing is effective and efficient.